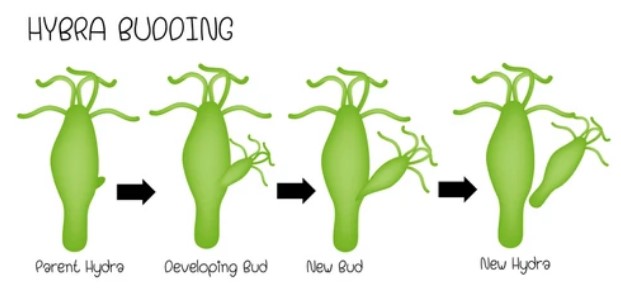
Budding
A bud, which is a tiny, bulbous outgrowth on the parent body, develops into a new organism throughout the process called budding. The bud separates from the parent and produces a new daughter cell.
Occasionally, another bud grows from the first bud, forming a chain of buds. If adequate resources and ideal circumstances are present, an organism will continue to grow and multiply every few hours if this process is sustained.
Budding is the method through which yeast, a fungal-like single-celled organism, reproduces.
Yeast growth happens every few hours if adequate resources and ideal conditions are present. Besides, Hydra is another organism that reproduces through the budding process too.
Fragmentation
Some water-dwelling algae (Spirogyra) reproduce by the process called fragmentation. In the process of fragmentation, the body of the parent plant splits into fragments, and each fragment develops into a new plant. Fragmentation of the parent body takes place as they reach maturity.
In the presence of water and nutrients, algae will grow and proliferate fast via fragmentation. If this process continues, a big area will be covered in a relatively short amount of time.
Spore development
Fungi such as bread mold reproduce asexually via the production of spores. Spores (found in the air) are tiny spherical entities with a protective coating that shields them from adverse circumstances. When proper circumstances are present, spores germinate and produce new plants.
Spores are very lightweight, asexually reproducing bodies that may travel great distances by air or wind.
Other plants, such as mosses and ferns, reproduce via spore production on the undersides of their leaves.
Spores have the ability to travel great distances when transported by the wind or air.
Reproduction in plants
Flowers are a plant's reproductive structure that aid plants in sexual reproduction and fruit and seed development.
In sexual reproduction, the male portion of a flower produces a male cell that fuses with a female cell generated by the female portion of the flower. These cells, known as gametes, combine to produce a zygote via a process known as fertilization.
Understanding various components of a flower
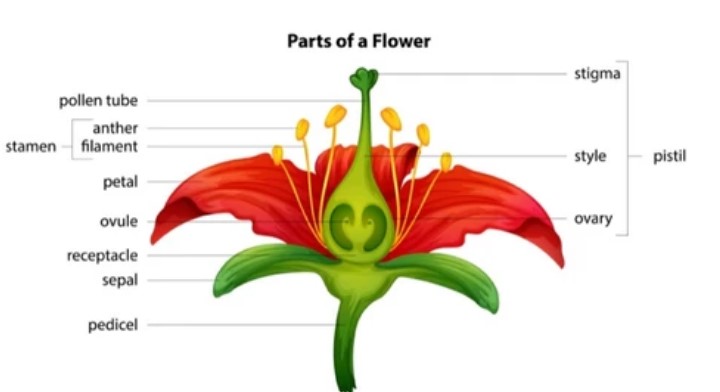
The essential components of a flower are as follows.
i) Sepals: This is the outermost circle of the flower, which looks like a green leaf. The collective term for the sepals is calyx. The calyx serves to protect the flower while it is in the bud stage.
(ii) Petals: These are the most vibrant and visually appealing component of the flower. These are found inside the sepals. The collective term for the petals is corolla. These are fragrant and attract pollinating insects.
(iii) Stamen: It is a plant's male reproductive organ that are the little, swollen-topped stalks seen inside the ring of petals.
The stamen consists of two components: the filament and anther. The stalk of a stamen is known as the filament, whereas the swelling tip of a stamen is known as the anther.
The anthers carry pollen grains containing male gametes. When the anthers mature and separate, pollen grains become exposed. These look as a yellow, powder-like material that is adhesive. Flowers often include a lot of stamens so that pollination becomes possible easily.
(iv) Pistil: The center of a flower contains the flower's female reproductive organs. There are three elements to this flask-shaped structure: the stigma, style, and ovary.
The stigma is the portion of the pistil at its apex. During the process of pollination, the grains of pollen are transferred to it from the anther. Within the centre of the pistil lies a tube-like structure known as the style that links the stigma to the ovary.
The swelling at the base of the pistil is known as the ovary that produces and stores ovules. These ovules are what are often referred to as egg cells since they carry the female sex cells, also known as flower's female gamete. The pistil, known as the carpel, is accompanied by many stamens.
The term "receptacle" refers to the component of the flower that serves as its foundation and to which all of the other sections of the flower are connected.
Different classifications of flowers
Based on the kind of reproductive organs present in a flower, the following categories of flowers may be distinguished.
i) Unisexual flower: Flowers with just one reproductive organ (male or female) are referred to as unisexual flowers. These are also known as incomplete flowers, including papaya, watermelon, maize, and cucumber, among others.
ii) Bisexual flower: The second kind of flower is the bisexual flower, which has both male and female reproductive structures inside a flower. These are also known as hermaphrodites or entire flowers, such as the rose, mustard, and Hibiscus.
FAQs
Q1. Which is the femal reproductive parts of a flower?
Ans. The stigma, style, and ovary make up the pistil, which is the female reproductive organ. The stigma is the uppermost portion of the pistil, followed by the style, which joins the stigma to the ovary (flower's base). The ovary is the swollen (lowest) portion of the pistil that contains egg-like ovules (one or several). In an ovule, the female gamete or the egg develops.
Q2. What are a flower's male reproductive parts? What is their function?
Ans. The male reproductive organs of a flower aid in sexual reproduction in order to create fruits and seeds. Stamens are the male component of a flower, consisting of anthers and filament (stalk of filament). Anthers hold pollen grains that generate male gametes. Pollen grains contain a protective coating that keeps them from drying out.
Q3. Can reproduction in big plants occur without the presence of flowers?
Ans. No, reproduction in big plants cannot occur without the presence of flowers. This is because flowers produce the essential female and male parts responsible for reproduction in plants.
Q4. Can you explain how flowers play a major role in reproduction in plants?
Ans. A flower's purpose is to produce both male and female gametes, as well as to facilitate fertilization and seed production. Male and female gametes combine to produce the zygote during the process of reproduction in plants.
To know more about Budding, Fragmentation, Spore development and Reproduction in plants, you can check out videos. We also create animated videos based on various syllabus, so call us if you would like to create animated videos.