You must be coming across different types of mirrors in your daily life. It is not necessary that all mirrors have to be flat or plane in nature. If you have seen the bicycle mirror or a vehicle's mirror, it is different from a flat mirror.
You may think, how you will come to know whether a mirror is flat or spherical in shape? All you have to do is touch it and you will notice that the mirror is slightly curved. Similarly, if you happen to go to a dentist, check out the mirrors they use. You will notice that even they use a slightly curved mirror that magnifies an object. Thus, a mirror that has a reflecting surface with a slight curve or part of a hollow sphere of glass is called a spherical mirror.
Types of spherical mirrors
Generally, spherical mirrors create reflections of the objects that are situated in front of them. You would notice that when light rays that seem to emerge out of the object and fall on a spherical mirror, the beam of light converges or diverges which leads to the formation of an image.
When we talk about spherical mirrors, there are two types of spherical mirrors we can consider and those are concave and convex mirrors.
A spoon may be used to illustrate the image production by a spherical mirror. That is, when you look at the spoon carefully, you will find that it has a hollow surface or a concave surface on one side, and on the other side, it has a protruding surface or convex surface.
Concave Mirror (Converging Mirror)
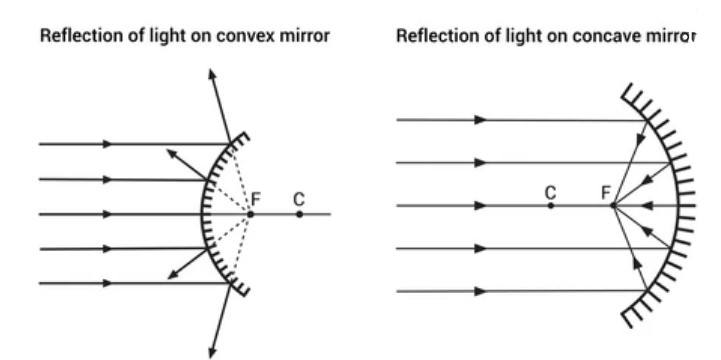
A concave mirror is one in which the reflecting surface is concave and the backside of the mirror is polished is convex in nature.
When parallel beams of light fall on a concave mirror, they converge all the beams of light to a single point which is called the focal (focus) point, and hence, it is also called a converging mirror. It is on the focus point on the concave surface that an image is formed.
Mirror image formation in a concave surface when an object is very far away
If you use a concave mirror, you may notice a real image of an object. We can comprehend the production of an image by a concave mirror when the object in question is far away and engaged in an activity.
When you keep an object far away from a concave surface, the image generated by a concave mirror is significantly smaller than the object (greatly decreased) and is real since it can be captured on paper (similar to a screen).
On the other hand, considering an object is kept at a great distance in front of a concave mirror, the resulting picture is real, inverted, and considerably smaller than the object itself.
Concave mirror image formation when an object is positioned near a concave mirror
Let's comprehend the generation of an image when an item is positioned near a concave mirror.
The image is virtual since it can only be perceived by staring into the concave mirror and cannot be generated on the screen.
Examining the image in the concave mirror reveals that it has the same orientation as the candle, hence the image is upright. Comparing the size of the candle and its picture reveals that the image is bigger than the candle. Consequently, the image is bigger than the actual thing (enlarged or magnified).
Therefore, when an object is positioned near a concave mirror, the image generated by the concave mirror is virtual, upright, and bigger than the object (bigger or magnified).
For what purposes concave mirrors are used?
Concave mirrors can be used wherever you want to magnify an object. Hence, it is used by dentists to look at the tooth and it is also used as a cosmetic or makeup mirror.
⦁ The dentist uses concave mirrors in order to view a huge picture of the patient's teeth.
⦁ Concave mirrors are employed as reflectors in various lighting devices (torches, car headlights, searchlights, etc.) to produce a powerful, straight beam of light.
⦁ To view a huge picture of the face, concave shaving mirrors are used.
Convex Reflector (Diverging Mirror)
The mirror with a bulging or convex reflecting surface (while the other end which is a polished surface has a concave surface) is known as a convex mirror.
After being reflected by the convex mirror, the parallel light beams are spread out or appear to diverge. When parallel light beams widen apart, we conclude that the light rays are moving further away from each other.
After reflection off a convex mirror, we may now state that a beam of parallel light rays diverges (tends to spread out).
Since a convex mirror causes parallel light beams to diverge, it is also referred to as a diverging mirror.
To learn more about spherical mirrors - concave and convex mirrors, you can check out our videos on them.


