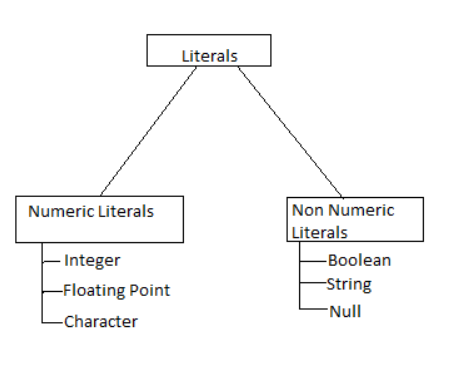
Literal and Addition of Literals
Definition
A literal number is a letter that symbolizes a number.
Understanding Literal
Mathematics uses arithmetical symbols to express quantities such as the digits, 4, 5, 6, 7, etc.
When introducing algebra, the same topicIdea is utilized, rather than numbers, symbols represent quantities instead. There are certain symbols that cannot be used to indicate numbers, such as, +, -, x. Letters such as those found in English, Greek, and other alphabets are used to denote numbers.
Literal numbers or literals are thus letters that express numbers. Algebraic literals are fundamental algebraic symbols that may be used to represent any quantity in algebra. However, we must indicate that the letter represents a specific number in order to prevent misunderstanding.
Examples of Literal
You may learn about literals in algebra by looking at these examples.
For example:
There are seven days in a week. To symbolize this number, you may use any letter.
W = 7 in this case, for example
Let's say you wish to symbolize the number of days in a week with the letter W. For whatever reason, W stands for "quantity." For this reason, in mathematics, the letter "w" is termed the literal.
As an example:
In a straight line, the angle is 180°.
In this case, angle Alpha = 180 degrees
As a literal number, the letter alpha is known as alpha.
Addition of literals
As with the addition of integers, adding literals obeys all of the same rules. Let's suppose we're requested to calculate the sum of two integers, say 2 and 6. The sum is expressed as 2 + 6 in numbers. Similarly, when you want to find out the total of y and 7, you may use y + 7, which is the same as saying "y plus 7.". Also, y + 7 may mean "7 more than y" and "increase by 7".
Similarly, if y is more than a literal x, x + y is used. Also, x + y may be interpreted as the total of x and y. As a result, ((x + y + z)) + ((y + z)) adds up the total of the two words in question, whereas (x + y+z) adds up x to the sum of the two words in question.
Suppose we have an algebraic object m, and we would want to add 25. The arithmetical equivalent is m + 25. m + n represents the addition of two quantities m and n. m + 25 is the sum of m and 25.
In the case of the sum of two literal numbers, it is represented as M+N (M+N).
The sum of m and m equals m + m = 2m.
The sum of m, n, and 5 is m + n + 5.
How to adding same literals?
Let's look at how to add two or more literals that are the same.
x + x = 2x
When adding x to the same literal x, it is treated as two same symbols. In this instance, there are two same symbols. As a result, the mathematical sum of two "x" symbols may be represented as 2x.
Arithmetic can also be used to prove it.
x + x = (1 * x) + (1 * x)
= x * (1+1)
= x * 2
= 2x
Similarly,
y + y + y = 3y
z + z + z + z = 4y
How to add different literals?
Let's look at how to add two or more literal together.
x + y
Two different literals with unknown values are x and y. It is therefore impossible to obtain their sum. Consequently, the sum of these two different literals can be expressed as an algebraic expression.
More Examples
a + b + c
Here, a, b, and c are unknown variables or literals.