All living creatures, including plants and animals, have the capacity to reproduce throughout their lifetime. This process of creating a new offspring or organism from an existing organism (or parent) of the same species is referred to as reproduction. The new offsprings that are created are exact replicas of their parents.
Why reproduction is necessary for organisms and what is its role?
Reproduction is a fundamental biological function that ensures the survival of a species. Thus, reproduction ensures the continuity of life, which is not only required for the survival of an organism, but also for the propagation and maintenance of the species, since it increases the number of individuals within a species.
Reproduction Methods
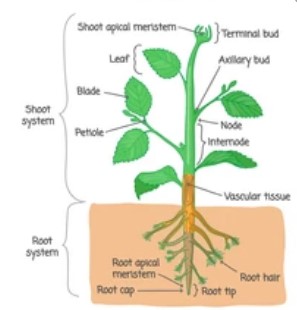
Vegetative components are the numerous sections of a plant, such as the roots, stem, and leaves, each having a distinct purpose. After a time of development, plants produce flowers, which later produce fruits and seeds.
Reproductive parts
The parts or structures of a plant that engage in sexual reproduction are referred to as reproductive parts.
Reproductive parts in plants
In plants, the reproductive parts would be present in flowers, which may be either male or female or both.
Reproduction in plants
There are two distinct processes of reproduction in plants:
⦁ Reproduction without sexual reproduction (Asexual) reproduction.
⦁ Sexual reproduction.
The term 'sexual' refers to the fusing of sex cells or gametes, while 'asexual' refers to the absence of such fusion.
Reproduction without asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is the act in which only one parent is engaged in the development of new offspring of the same species. Asexual reproduction in plants leads to the development of offspring or new plants devoid of seeds or spores.
The following asexual reproductive mechanisms are found in plants, and we will examine each of them separately:
⦁ Vegetative propagation
⦁ Budding
⦁ Fragmentation
⦁ Spore development
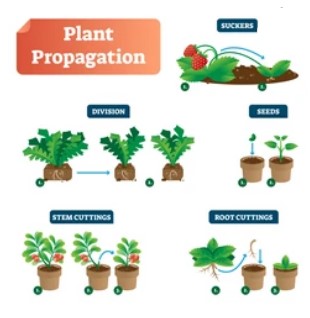
1. Vegetative Propagation
It is the development of new plants from vegetative units like buds, stems, etc., and these plant components are known as propagules. Various plant components, as listed below, are capable of vegetative reproduction.
Stem-Based Vegetative Reproduction
The axils of the stems or branches of the plant often yield buds. The shoot grows from the axillary buds (i.e., the growth area of the leaf at the node) and they are referred to as vegetative buds.
The vegetative buds are capable of producing a new plant. These buds are made up of a small stem that has immature leaves that overlap and are folded neatly within each other. These are capable of producing new plants by vegetative propagation.
Plant propagation by stem modification
The modified stems of plants are known as tuberous stems, which have nodes that yield buds that may develop into new plants.
When a potato is placed in the soil, each of its buds, known as eyes (which resemble scars), might develop into a new plant.
Tubers (stem or root) have the capacity to store nutrients or food. Other examples of tuber plants are ginger and turmeric, both of which contain buds on their stem tubers.
Methods of Vegetative Stem Reproduction
⦁ Cutting technique: Using the procedure of cutting, new plants are produced from the stem. Using a sharp knife, the little portion of the stem is removed in this technique. The stem cutting must include a few buds. The base of the stem cutting is now covered in damp soil. The bud-bearing portion of a cutting is preserved above the soil. After a few days, new roots emerge on this cutting. The bloom develops and produces a shoot (i.e., leaves-bearing branches) Thus, a new plant is created that is identical to the original plant, such as a rose, grapes, sugarcane, or cactus.
⦁ Layering: Layering is another technique for vegetative reproduction in stems. In this technique, a mature branch is twisted and put inside the soil, with the plant tip remaining above the ground. From the branches, the root develops and matures into a new plant. Typically, the layering approach is used on plants with long, thin branches, such as jasmine.
⦁ Grafting: Grafting is also a technique of vegetative reproduction in stems, in which new plants with the required characteristics are created by combining two distinct plants. The section with shoots is termed scion, whereas the part with roots is called stock. Scion is related to the stock that gives support and fundamental needs for the growth of a plant, such as mango, apple, rose, etc.
Reproduction of Plants via Leaves
When the leaves of some plants are deposited into damp soil, the cut edges or margins of the leaves grow into new plants that mimic the original plant, e.g. sprout leaf plant or Bryopbyllum.
Reproduction of plants via their roots and bulbs
Some plants, such as sweet potato and dahlia, produce a new plant via their roots and bulbs.
Positive aspects of vegetative propagation
Plants grown by vegetative reproduction need less time to mature and produce flowers and fruit sooner than those grown from seeds.
Because they are created from a single parent, the offspring are identical replicas of the parent plant.
Summary of vegetative propagation:
Vegetative propagation can be stem cuttings, modified stem, leaf, and root cuttings.
Examples of stem cuttings include sugarcane, rose, champa, grapes, banana, jasmine, and cactus.
Examples of modified stems include potato, turmeric, and ginger.
Examples of Leaf include Bryophyllum.
Examples of Root cuttings include sweet potato, dahlia, and blackberry.
FAQ:
Q1. Can we grow cactus by cutting a portion of it?
Ans. Yes, plants such as cactus develop new plants when their components get separated from the main plant body. Each separated portion might develop as a separate plant.
Q2. How to perform vegetative propagation using the stem cutting method?
Ans. Here are the steps provided to perform vegetative propagation using the stem cutting method.
⦁ Using a knife, a tiny portion of the stem with a node is removed.
⦁ Please ensure that the stem cutting must include buds.
⦁ The lower end of a stem cutting is inserted or buried in the soil, while the bud-bearing portion is positioned above the soil.
⦁ After a few days, new roots form on the cutting.
⦁ The bud develops and produces a shoot. This produces a new plant that is similar to the parent plant.
This method is appropriate for plants such as rose, money plant, champa, banana, sugarcane, and other plants.
To know more about reproduction in plants or methods of vegetative propagation, check out our videos.